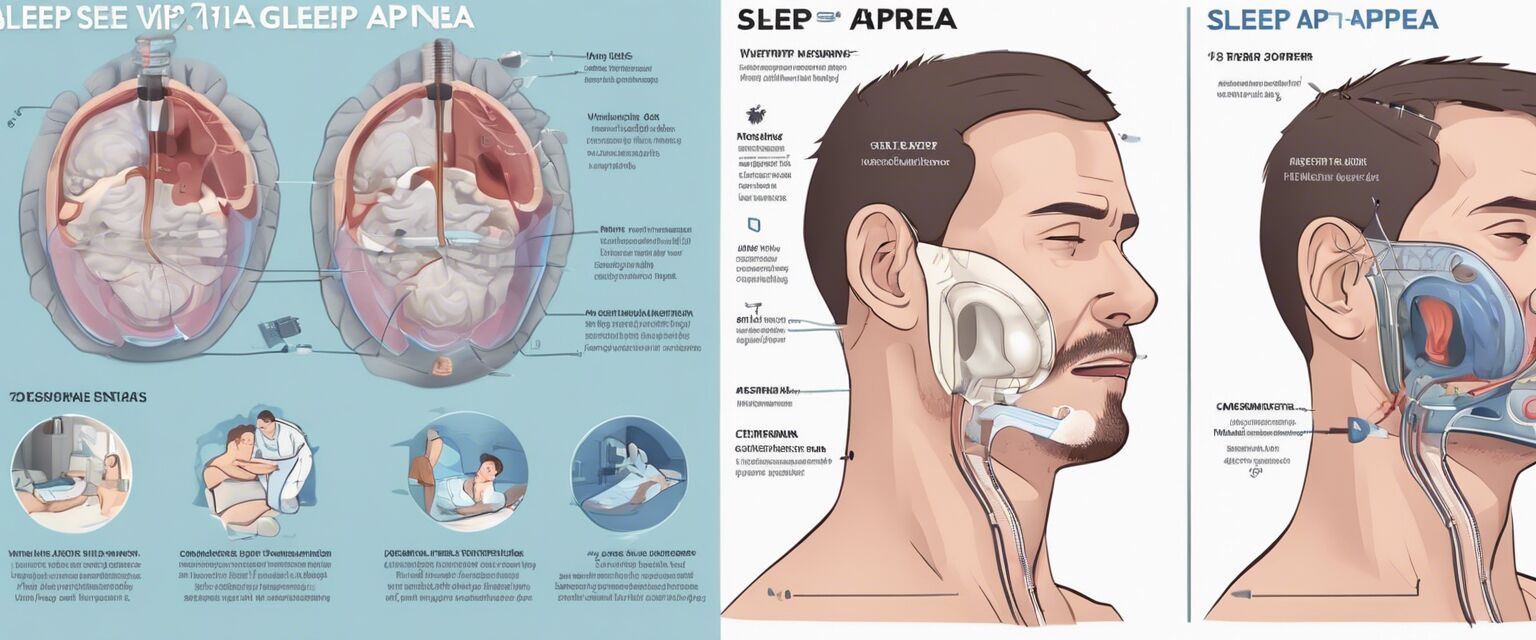
Surgical Treatments
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the types of surgical treatments available for sleep apnea.
- Evaluating the effectiveness and risks associated with each surgical option.
- Considering the pre-operative and post-operative care for better outcomes.
Sleep apnea can significantly affect your quality of life, and for some individuals, surgical intervention may be necessary. This article provides an overview of various surgical options available for treating sleep apnea, including their effectiveness, risks, and what to expect during recovery.
What is sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that occurs when a person's breathing is interrupted during sleep. It can lead to various health complications if left untreated. Understanding different treatment options, including surgical treatments, is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Surgical Options for Treating Sleep Apnea
Various surgical options are available for treating sleep apnea, especially for those who do not respond well to CPAP therapy or other non-invasive treatments. Below are some common surgical procedures:
| Surgical Procedure | Description | Ideal Candidates | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) | A procedure that removes excess tissue from the throat to widen the airway. | Patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea. | Bleeding, infection, changes in voice. |
| Genioglossus Advancement | Repositioning the tongue muscle attachment to prevent airway obstruction. | Patients with retrognathia. | Swelling, discomfort, potential jaw problems. |
| Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA) | Repositioning the upper and lower jaw to enlarge the airway. | Patients with skeletal issues contributing to apnea. | Jaw pain, nerve injury, longer recovery time. |
| Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation | A device is implanted to stimulate the hypoglossal nerve and keep the airway open during sleep. | Patients with moderate obstructive sleep apnea who cannot use CPAP. | Infection, device malfunction, discomfort. |
| Tracheostomy | Creating an opening in the neck to bypass the obstructed airway. | Severe cases where other treatments have failed. | Infection, changes in voice, psychological effects. |
Pre-operative Considerations
Before undergoing surgery for sleep apnea, it is essential to have a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional. This may include:
- Sleep studies to determine the severity of sleep apnea.
- Consultation with an ENT specialist.
- Discussion of medical history and any other health concerns.
Post-operative Care
Post-operative care is critical for recovery and successful outcomes. Here are some common guidelines:
- Follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider.
- Adhere to prescribed medications for pain management.
- Monitor for any signs of infection or complications.
- Gradually resume normal activities as directed.
Pros
- Potential long-term relief from sleep apnea symptoms.
- Improvement in quality of life and daytime alertness.
- Reduction in associated health risks.
Cons
- Invasive nature of surgical procedures.
- Possible complications and side effects.
- Need for a recovery period.
Alternatives to Surgery
Not all patients may require surgery. There are several non-invasive treatment options available, such as:
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy.
- Oral appliances to reposition the jaw.
- Lifestyle changes including weight management and avoiding alcohol.
For more information on lifestyle changes, check our Lifestyle Changes page.
Conclusion
Surgical treatments for sleep apnea can provide effective solutions for those who have not found relief through other means. It is essential to work closely with healthcare providers to determine the best course of action based on individual needs and conditions.
For additional support and information on managing sleep apnea, explore our Sleep Apnea Devices or Natural Sleep Aids sections.
Further Reading
To understand more about sleep apnea and its treatments, consider visiting:
Image Gallery
Below are some illustrative images related to surgical treatments for sleep apnea: